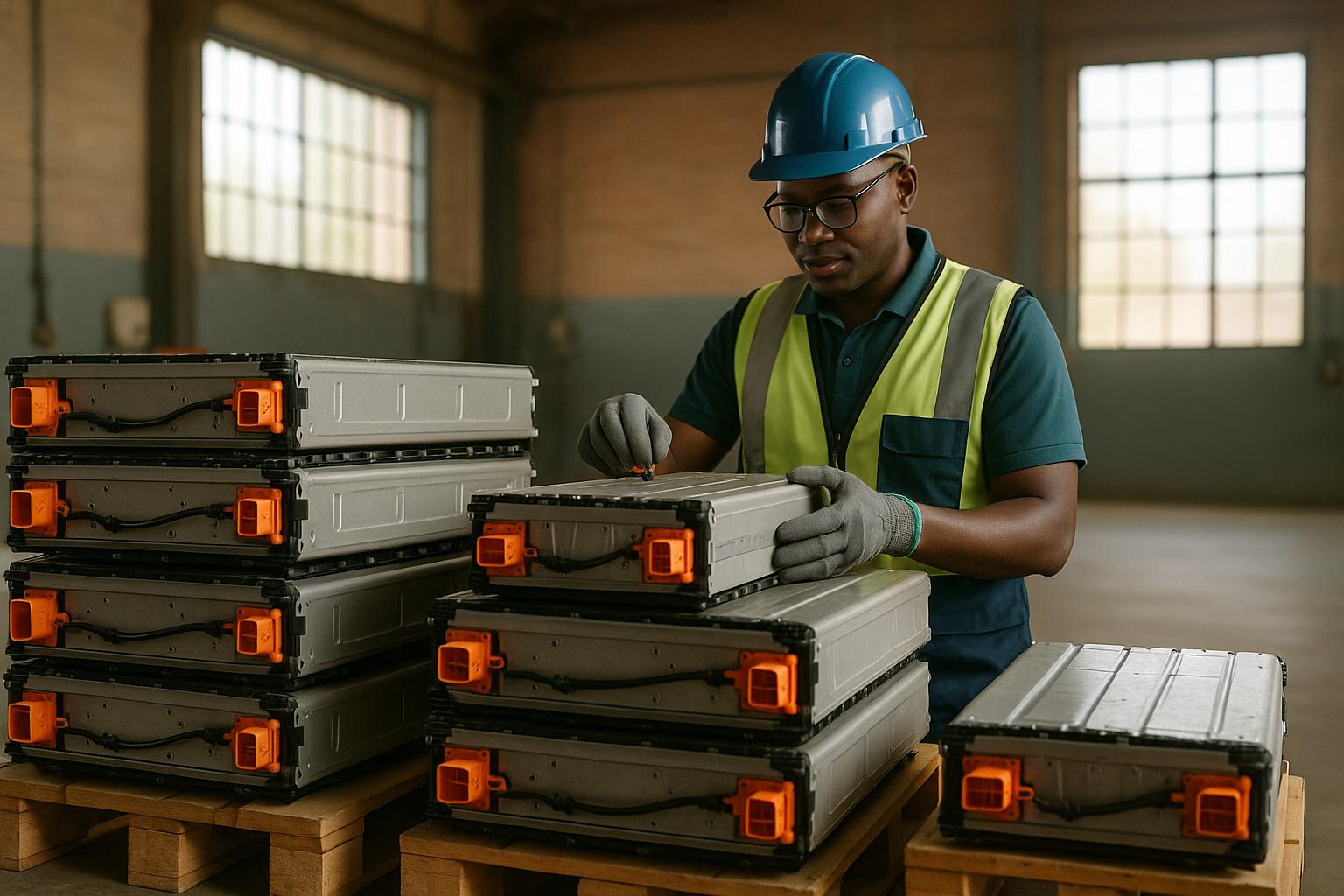
Second-life EV batteries are used electric vehicle (EV) batteries that are repurposed for non-automotive applications like energy storage for homes, businesses, and grids. These batteries are gaining traction in Africa due to their affordability and potential to support renewable energy projects, improve electricity access, and stabilize grids. However, the lack of clear regulations poses challenges related to safety, trade, and environmental concerns.
Key points covered in this article:
- Why regulations are needed: To ensure safety, manage waste, and create jobs in testing, refurbishment, and recycling.
- Current state of regulations: Countries like Kenya and South Africa are leading with specific standards, while others rely on general environmental or electrical rules.
- Challenges: Limited enforcement, fragmented policies, and informal markets hinder progress.
- Opportunities: Aligning rules across Africa, using digital tracking tools, and promoting public-private partnerships could address these gaps.
- Case studies: Kenya focuses on battery traceability, while South Africa emphasizes refurbishment standards.
The article also highlights platforms like EV24.africa, which simplify compliance and cross-border trade by standardizing documentation and ensuring regulatory alignment. As the market evolves, harmonized policies and transparent practices will be crucial for growth.
Current Regulations for Second-Life EV Batteries
National Regulations and Standards
In Africa, the regulatory landscape for second-life EV batteries is still taking shape. Many countries rely on existing rules for environmental protection or electrical equipment, which often don’t fully address the unique aspects of repurposed batteries. To address this gap, several nations are working on creating specific standards and guidelines, though progress varies widely across the continent. These national efforts are laying the groundwork for broader regional and international standards.
Regional and International Guidelines
In the absence of universal standards, African countries are adopting a mix of approaches. Many draw inspiration from established frameworks like those of the IEC and IEEE, as well as newer policies such as the European Union’s upcoming 2026 battery passport initiative and China’s safety-focused measures.
Regulatory Gaps and Challenges
One of the biggest hurdles in Africa is the lack of a unified regulatory framework for second-life EV batteries. The differences in national policies can make cross-border trade and market integration more complicated. This patchwork of regulations highlights the pressing need for consistent standards that address safety, performance, and the management of batteries at the end of their life cycle.
The SEI at EUC Presents: Post-Consumer Management of EV Batteries
Compliance Requirements for Buyers and Sellers
Compliance requirements play a crucial role in guiding buyers and sellers through the maze of legal certifications and documentation. When it comes to second-life EV batteries in Africa, ensuring proper legal certification and maintaining accurate documentation is essential for both imports and local sales.
Product Testing and Certification
To sell repurposed batteries in markets that adhere to international standards, homologation (or type approval) is a must. One key standard in this field is UNECE Regulation No. 100, specifically the second revision (ECE R100.02). This regulation ensures that repurposed batteries meet stringent safety and performance criteria, providing confidence in their reliability.
Import/Export and Documentation Requirements
For cross-border trade, importers and exporters need to obtain permits and compliance certificates. These documents confirm that the batteries meet international standards, paving the way for smoother transactions and market entry.
Warranties, Liability, and End-of-Life Responsibilities
Warranties and liability agreements, along with clear end-of-life responsibilities, are essential considerations in the second-life EV battery market. These measures help protect buyers and sellers while ensuring environmental and legal obligations are met effectively.
sbb-itb-99e19e3
Policy Implementation Challenges and Opportunities
Turning policies into action is where the real work begins, especially in the second-life EV battery trade across Africa’s diverse regulatory environment. As mentioned earlier, regulatory gaps and enforcement challenges remain significant hurdles. Adding to this complexity are practical issues like limited oversight and fragmented markets. Let’s dive into these challenges and explore practical ways to address them.
Regulatory Challenges
One of the biggest obstacles is the lack of enforcement infrastructure. Many countries simply don’t have the resources, systems, or technical know-how to ensure compliance. This creates an uneven playing field where businesses operating under stricter guidelines often face higher costs compared to those in loosely regulated environments.
The informal market adds another layer of difficulty. A substantial number of second-life battery transactions happen through informal channels, where traditional oversight is nearly impossible. This makes it harder to track the lifecycle of batteries and ensure they are disposed of responsibly at the end of their use.
Opportunities for Policy and Market Development
There’s a real chance to improve how policies are implemented by harmonizing regulations across African markets. Standardizing safety tests and documentation would help reduce trade barriers. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) offers a promising framework to support this kind of regulatory alignment.
Digital tracking systems could also revolutionize oversight. By using tools like blockchain, it becomes easier to monitor a battery’s journey – from its first use to its second life and, eventually, recycling. This would make cross-border verification more reliable and efficient.
Investing in capacity building is another important step. Training programs for regulatory staff, supported by international organizations, can enhance skills in areas like battery testing and risk assessment. This not only strengthens enforcement but also builds local expertise.
Public-private partnerships can be a game-changer as well. By pooling resources, these collaborations can create shared testing facilities and streamline procedures, making compliance easier and supporting market growth.
Diverse Regulatory Approaches and the Path Forward
African markets vary widely in their regulatory readiness, but shared challenges like limited expertise and resource constraints highlight the need for regional cooperation. By working together and sharing knowledge, countries can tackle these issues more effectively. Moving forward, striking a balance between strict regulations and practical enforcement will be key to fostering market growth while ensuring consumer safety and environmental protection.
Case Studies: Regulatory Practices in Action
Kenya: Building a Circular Battery Economy
Kenya has taken a forward-thinking approach to managing the lifecycle of batteries, implementing a closed-loop system. Here’s how it works: batteries are first used in vehicles, then repurposed for stationary energy storage, and finally sent for recycling at the end of their life.
To ensure safety and reliability, the Kenya Bureau of Standards (KEBS) has set up detailed testing protocols. These tests verify that second-life batteries retain enough of their original capacity for secondary uses. Additionally, KEBS mandates full traceability, requiring documentation of each battery’s original use, age, charging cycles, and performance. This transparent system not only builds trust among consumers but also simplifies evaluations for local energy storage projects.
While Kenya prioritizes lifecycle traceability, South Africa has focused on refurbishment and creating distinct market models.
South Africa: Clear Guidelines for Refurbishment
South Africa has developed a regulatory framework that supports battery refurbishment by setting clear distinctions between repurposing and refurbishing. Refurbishing involves thorough reconditioning to improve battery performance, going beyond basic reuse.
To operate legally, refurbishment facilities must secure licenses and comply with strict safety and testing standards. These regulations ensure that facilities are equipped with proper equipment, skilled technicians, and protocols for safely handling and disposing of defective cells. This framework not only prioritizes safety but also encourages collaboration between manufacturers and refurbishment operators, creating a market that values both reliability and innovation.
EV24.africa: Pioneering Compliance in Africa
EV24.africa, an online marketplace for electric vehicles spanning 54 African countries, plays a vital role in ensuring regulatory compliance within the second-life EV battery market. The platform requires sellers to provide detailed documentation, including battery capacity assessments, safety certifications, and proof of compliance with local regulations. This helps buyers make well-informed decisions and strengthens trust in the second-life battery market.
Additionally, EV24.africa simplifies cross-border trade by standardizing documentation requirements and ensuring batteries meet the destination country’s regulatory standards. With its extensive network and delivery services, the platform reduces trade barriers while maintaining high safety and quality benchmarks, paving the way for a more transparent and efficient market across Africa.
Key Takeaways and Future Outlook
The regulatory environment for second-life EV batteries in Africa is shifting, bringing new opportunities and challenges for buyers, sellers, and the broader EV ecosystem. Navigating these frameworks is becoming increasingly important for anyone involved in this emerging market.
Clear regulatory standards, as seen in Kenya and South Africa, can drive both market growth and safety. Kenya’s traceability system and South Africa’s licensing for refurbishment highlight how well-structured regulations can support progress rather than stifle it.
However, gaps in regulations create obstacles for cross-border trade. At the same time, these gaps present a chance for countries to align their policies, learning from early adopters to avoid common mistakes. Harmonized regulations could simplify trade and foster collaboration across the continent.
As the market evolves, thorough documentation – covering battery histories, certifications, and warranties – will become a key differentiator. Companies that prioritize this level of transparency will gain a competitive edge.
Digital platforms like EV24.africa are already stepping in to address regulatory inconsistencies. By providing standardized documentation and ensuring compliance across Africa’s 54 countries, these platforms demonstrate how technology can uphold safety while enabling trade.
Looking ahead, aligning with international standards will likely attract more investment and streamline trade processes. Additionally, growing attention to lifecycle management and circular economy principles will make end-of-life responsibilities a critical focus.
As regulations continue to develop, the second-life EV battery market in Africa is poised for growth. Organizations that emphasize compliance, transparency, and sustainability will be at the forefront of this expansion.
FAQs
What are the main challenges and opportunities in regulating second-life EV batteries in Africa?
The regulation of second-life EV batteries in Africa comes with its fair share of hurdles. For starters, there’s the challenge of dealing with the sheer variety of battery types, each with its own specifications. On top of that, transporting these batteries can be incredibly expensive, and ensuring they meet quality benchmarks – like retaining at least 80% of their original capacity for reuse – adds another layer of complexity. To make matters trickier, the absence of clear, unified policies across the continent creates a fragmented regulatory landscape.
But it’s not all obstacles – there’s plenty of potential, too. By putting solid regulations in place, Africa has a chance to champion energy solutions that last, cut down on electronic waste, and build a circular economy that keeps resources in use longer. Standardized practices could also pave the way for investments in infrastructure, especially for using second-life batteries in energy storage systems for homes and businesses. The key to unlocking these opportunities lies in establishing clear, harmonized policies that ensure the safe and effective use of second-life EV batteries across the region.
How do Kenya and South Africa regulate second-life EV batteries differently?
Kenya is exploring innovative ways to repurpose second-life EV batteries, focusing on critical applications in schools and hospitals. Their regulatory framework highlights safety standards and extended producer responsibility (EPR), ensuring these batteries are handled and reused responsibly.
Meanwhile, South Africa is prioritizing battery recycling and sustainable practices. The government has set ambitious targets, such as achieving a 20% EV market share by 2030. Their regulations aim to promote environmental responsibility while fostering long-term growth in the EV sector.
Kenya’s strategy leans toward practical applications, while South Africa’s policies are shaped by broader environmental and economic goals.
How does EV24.africa ensure compliance and support cross-border trade for second-life EV batteries in Africa?
EV24.africa is dedicated to ensuring that second-life EV batteries meet regulatory standards across Africa. By pushing for unified policies and clear safety guidelines, the platform not only simplifies cross-border trade but also ensures that safety and environmental standards are consistently maintained.
Beyond policy advocacy, EV24.africa creates a reliable marketplace where buyers and sellers can connect with confidence. Through access to trustworthy information and resources, the platform promotes responsible trading practices. This approach helps build a sustainable and transparent ecosystem for second-life EV batteries, making international transactions smoother and more secure.