Looking to buy an electric vehicle (EV) in 2026? Here’s what you need to know about LFP batteries, fast charging, and battery health:
- LFP Batteries Are Affordable and Durable:
- Cost about 6% less per kilowatt-hour than nickel-based batteries.
- Last longer, with 3,000–10,000+ charging cycles.
- Safer in hot climates, making them ideal for African regions.
- Fast Charging Is Evolving:
- LFP batteries handle frequent fast charging better than nickel-based ones.
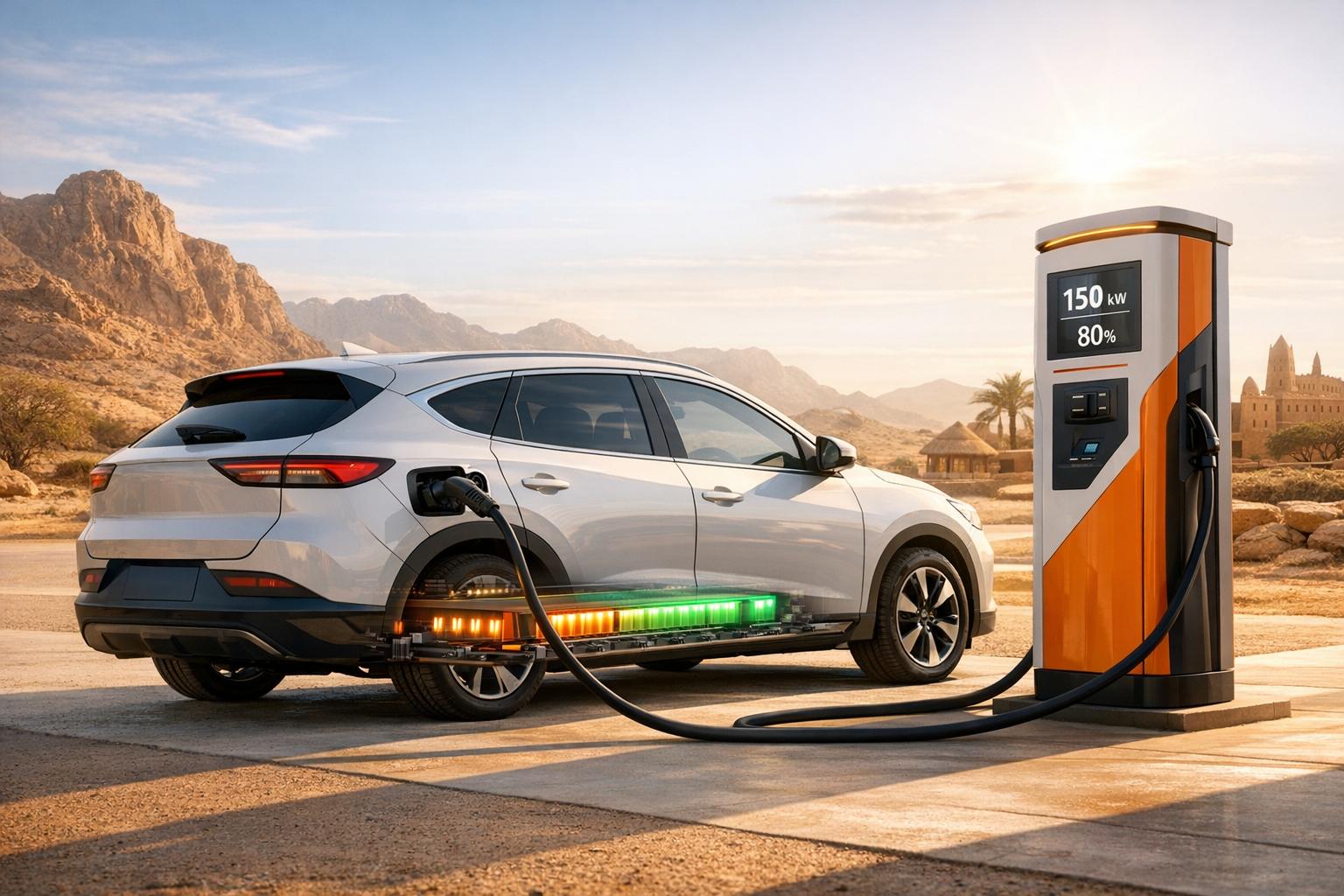
- CATL‘s Shenxing Plus can add 372 miles of range in just 10 minutes.
- Best practice: Charge to 80% for faster sessions and preserve battery life.
- Maintenance Tips for Long Battery Life:
- Charge to 100% weekly or monthly to recalibrate range estimates.
- Avoid keeping the battery fully charged in extreme heat.
- Store at 50% charge if the car will be unused for weeks.
- LFP vs. Nickel-Based Batteries:
- LFP is cheaper, safer, and lasts longer but offers lower energy density.
- Nickel-based options are better for long-range and cold climates.
- EV Tools for African Buyers:
- Platforms like EV24.africa simplify comparing LFP-equipped EVs, pricing, and delivery options across Africa.
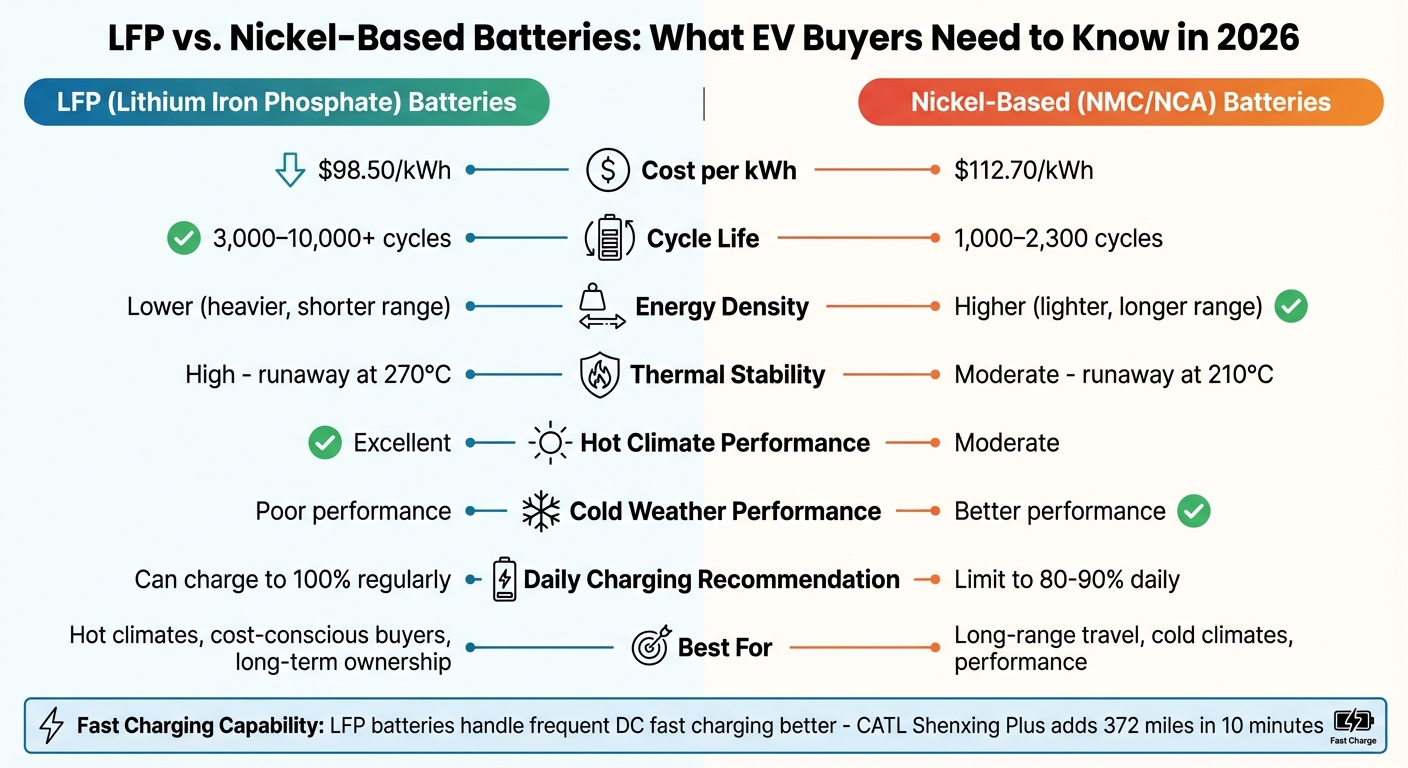
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | LFP Batteries | Nickel-Based Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | ~$98.50/kWh | ~$112.70/kWh |
| Cycle Life | 3,000–10,000+ cycles | 1,000–2,300 cycles |
| Energy Density | Lower (heavier, shorter range) | Higher (lighter, longer range) |
| Thermal Stability | High (better for hot climates) | Moderate |
| Cold Weather | Poor performance | Better performance |
LFP batteries are a great choice for affordability, safety, and durability, especially in warmer regions. But for long-range or cold conditions, nickel-based batteries might suit you better. Smart charging habits and understanding your battery type can save you money and extend the life of your EV.
LFP vs Nickel-Based EV Batteries: Complete Comparison 2026
Should You Charge an LFP Powered EV to 100% or 80%? Simple EV Math with Recurrent
What Makes LFP Batteries Different
LFP batteries differ from traditional nickel-based chemistries in three key ways: they are safer, last longer, and cost less. Instead of relying on nickel and cobalt, these batteries use iron and phosphate. This composition creates a more stable structure, as the phosphate ion’s strong P–O bond resists thermal runaway and avoids releasing oxygen, even if the battery is damaged.
When it comes to cost, LFP batteries are notably cheaper, averaging about $100 per kilowatt-hour compared to $160 for NMC batteries – a production cost savings of 20%. Some Chinese manufacturers even managed to procure LFP cells for as little as $56/kWh in early 2024. Longevity is another standout feature, with LFP batteries delivering between 2,500 and over 10,000 charge cycles, far surpassing the 1,000 to 2,300 cycles typical of NMC batteries.
LFP batteries also have a "flat voltage curve", meaning their voltage remains steady regardless of the charge level. While this stability is beneficial, it can make it harder for a vehicle’s computer to estimate the remaining range accurately. To address this, manufacturers recommend periodic full charges – Tesla suggests doing so weekly, while Ford advises a monthly full charge.
"LFP batteries hold up better to high states of charge, meaning that regularly charging them to 100% may not cause as much degradation as it would with a different battery chemistry." – Recurrent
Safety, Cost, and Durability
LFP batteries operate effectively across a wide temperature range, from –4°F (-20°C) to 140°F (60°C). Unlike nickel-based chemistries, they don’t break down at high temperatures, making them well-suited for areas with extreme heat, such as many African cities. For example, CATL LFP batteries used in the Zhangbei National Wind-Solar-Storage Demonstration Project in China retained over 90% of their capacity after 14 years of continuous use. Similarly, a Morgan Stanley test in January 2026 showed that CATL LFP batteries could maintain a range of approximately 248 miles (400 km) even after 1.24 million miles (2 million kilometers) of driving.
Another advantage of LFP batteries is their reliance on abundant materials like iron, the fourth most common element in Earth’s crust. This ensures a stable supply chain and scalable production, which lowers costs and bypasses the ethical and supply chain issues tied to cobalt mining. For consumers, this translates into lower long-term ownership costs and reduced maintenance concerns.
How LFP Batteries Perform in Different Climates
LFP batteries shine in hot climates, making them ideal for much of Africa. Their thermal stability reduces the need for complex cooling systems, cutting down on both weight and maintenance expenses. In cities like Lagos, Nairobi, or Johannesburg, LFP batteries perform consistently without the degradation issues that nickel-based chemistries often face in high temperatures.
However, these batteries are less efficient in cold environments, where performance can drop significantly. While this isn’t a major issue in most African regions, it could affect areas with cooler climates or high altitudes. To counteract this, modern EVs equipped with LFP batteries often include heating systems to maintain efficiency during colder months. For everyday driving – like short trips and urban commutes – LFP batteries excel, especially since they handle regular full charges without significant wear. This simplifies charging routines, which is particularly useful for those with limited access to fast chargers.
EV Models Using LFP Batteries in 2026
The affordability, safety, and durability of LFP batteries have led to their widespread adoption in many EV models. Tesla incorporates LFP packs in its Model 3 Standard Range and Model Y Standard Range, helping to keep these models more budget-friendly. Ford offers LFP options in select trims of its Mustang Mach‑E. BYD has gone all-in on LFP chemistry, using it across its lineup, including models like the Atto 3 and Seal. In 2023, Rivian announced plans to switch its standard-range R1T and R1S models to LFP technology to cut costs.
Chinese automakers are also heavily investing in LFP batteries. Companies like Geely, through its subsidiaries Zeekr and Polestar, and Leapmotor have introduced models equipped with this chemistry. In June 2025, CATL began mass-producing its 587 Ah cells at the Jining plant, achieving a production capacity of over 220,000 cells per day. These cells, produced with cycle times under 2 seconds, cost 42% less than earlier versions, driving down prices across the EV industry.
For those shopping for EVs in Africa, platforms like EV24.africa make it easy to filter vehicles by battery type. The site provides detailed specifications, including battery chemistry, kilowatt-hour capacity, and estimated range, along with pricing and delivery timelines tailored to all 54 African countries.
Fast Charging with LFP Batteries
LFP batteries shine when it comes to fast charging, making them a great choice for drivers who depend on public charging stations. Their stable structure handles the heat and voltage stress of high-power charging exceptionally well, allowing frequent DC fast charging without significantly affecting the battery’s lifespan. This reliability is especially important in African markets, where home charging access might be limited, and public charging networks are still growing. Let’s dive into charging speeds, connector types, and how these batteries perform under fast-charging conditions.
Charging Speeds and Connector Types
EV charging happens at three levels:
- Level 1: Uses a standard 120V household outlet, adding about 2–5 miles of range per hour.
- Level 2: Operates at 208V–240V, delivering 10–25 miles of range per hour, making it ideal for overnight charging.
- Level 3 (DC Fast Charging): Works at 400V–1,000V and can charge a battery to 80% in 20 minutes to an hour, adding 180–240 miles in just 30 minutes.
Connector types depend on region and manufacturer. In North America, J1772 is standard for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, while CCS (Combined Charging System) dominates DC fast charging. Japanese models often use CHAdeMO, and Tesla’s J3400 (NACS) connector is becoming an industry standard, opening up the Supercharger network to non-Tesla EVs. In Africa, CCS2 is more common at public stations, so checking your EV’s connector compatibility before heading out is a smart move.
LFP batteries charge using a Constant Current – Constant Voltage (CC-CV) profile, stopping when the current drops to about 0.05C. One unique feature of LFP batteries is their flat voltage curve, which makes it harder for the car’s system to estimate the remaining charge. This charging behavior directly impacts performance during fast charging.
How Fast Charging Affects LFP Batteries
LFP batteries handle frequent fast charging better than nickel-based alternatives. Their strong chemical structure and thermal stability minimize the risk of degradation, even with regular use of high-power chargers. However, charging speeds slow significantly after reaching 80% capacity. This slowdown, known as "tapering", is designed to protect the cells from overheating and overvoltage, but it means the final 20% takes as long as the first 80%.
While automakers suggest fully charging the battery occasionally for calibration, consistently keeping the charge between 75% and 100% can lead to faster degradation due to heat and high voltage. The best approach? Charge to 100% only when necessary and avoid frequent small top-ups at high charge levels.
| Feature | LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Charge Limit | 100% (occasionally for calibration) | 80–90% recommended |
| Fast Charging Durability | High (long cycle life) | Moderate (heat-sensitive) |
| Energy Density | Lower (heavier, shorter range) | Higher (longer range) |
| Safety | Excellent thermal stability | Moderate thermal stability |
| Cold Weather Performance | Higher performance loss | Better in cold climates |
Sources:
CATL’s Shenxing Plus LFP battery highlights how far this technology has come, claiming to add 372 miles (around 600 km) of range in just 10 minutes of charging. While this isn’t yet standard across all LFP-equipped EVs, it’s a sign of what’s possible in the near future.
Fast-Charging Stations in Africa
Africa’s public charging network is still in its early stages, with most stations concentrated in urban hubs like Lagos, Nairobi, Johannesburg, and Cape Town. DC fast chargers are the best option for long-distance travel, but their availability outside major cities is limited. Power output at these stations can vary, typically ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW.
EV owners in Africa need to plan ahead. Apps like PlugShare can help locate compatible fast chargers. Globally, only 55% of consumers have access to home charging, so public fast-charging infrastructure plays a critical role in EV adoption. According to the International Energy Agency, the number of public charging points worldwide is expected to quadruple by 2030, reaching 15 million.
"Large-scale adoption of EVs hinges on the simultaneous roll-out of accessible and affordable charging." – IEA (International Energy Agency)
For African EV drivers, a mix of home charging and public fast charging is key. Charging to 80% at a DC fast charger before continuing your trip is the most time-efficient strategy, as the last 20% takes considerably longer. As charging networks expand, particularly along major highways, long-distance EV travel will become increasingly practical across the continent.
sbb-itb-99e19e3
How to Maintain Your LFP Battery
After exploring the role of fast charging, it’s clear that proper maintenance is key to preserving battery performance. While LFP batteries are known for their durability, how you charge and store them has a big impact on their lifespan. On average, most modern EV batteries retain 80% to 90% of their original range after 8 to 10 years under normal use, with LFP batteries losing about 1.8% to 2.3% of their capacity annually. In regions with hot climates, like many parts of Africa, battery wear is an even bigger concern. A few simple precautions can go a long way in protecting your battery and keeping it running efficiently.
What Contributes to LFP Battery Wear
Several factors accelerate the aging process of LFP batteries, including high states of charge, extreme heat, and frequent use of high-power fast charging. Research shows that operating the battery near 75%–100% charge levels significantly speeds up degradation. Dr. Jeff Dahn’s team at Dalhousie University found that "cycling near the top of charge (75%–100% SoC) is detrimental to LFP/graphite cells. Our results show a correlation between the average SoC of battery operation and capacity fade rate".
The challenge is even greater in hot climates. When temperatures exceed 86°F (30°C), the chemical reactions inside the battery speed up, leading to faster lithium depletion. High heat combined with high voltage creates stress on the battery, causing electrolyte breakdown and iron loss.
Thankfully, your vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS) is designed to help manage these risks. It prevents overcharging, ensures cell balancing, and activates cooling systems to avoid overheating. Keeping your car’s software up to date is crucial, as newer charging algorithms can help maintain battery health over time.
Smart Charging Practices for LFP Batteries
To extend the life of your LFP battery, set your daily charge limit to 80% instead of 100%. Charge to 80% daily, but perform a full 100% charge either weekly (as Tesla advises) or monthly (as Ford recommends) to recalibrate the battery’s range estimation. Ford cautions that "if not charged to 100% at least once per month, you may experience degraded vehicle performance and a decrease in the accuracy of the vehicle’s estimated range".
If you’re planning to store your EV for several weeks, adjust your approach. Store the car at 50% charge in a cool, well-ventilated space. This charge level reduces chemical stress while preventing the battery from draining too much. Avoid leaving your car fully charged for extended periods in hot weather, as high voltage combined with heat accelerates aging.
For everyday use, rely on AC charging (Level 1 or Level 2) and reserve DC fast charging for long trips. While LFP batteries can handle fast charging well, slower charging generates less heat and reduces stress on the battery cells. In hot climates, make it a habit to park in shaded areas and, if possible, leave your car plugged in. Many EVs with active thermal management will automatically cool the battery when connected to a charger.
Next, we’ll explore how to monitor your battery’s health and detect early signs of wear.
Monitoring Your Battery’s Health
LFP batteries have a flat voltage curve between 25%–85%, which makes precise energy estimation tricky. Performing a full charge provides a useful baseline for recalibrating the system.
Compare your EV’s displayed range at 100% charge to its original factory rating. A small decrease in range is normal, but a significant drop might signal faster-than-expected degradation.
If you’re buying a used EV from platforms like EV24.africa, ask for a professional battery health report instead of relying solely on the dashboard display. Most automakers guarantee their batteries will retain at least 70% of their capacity for 8 to 10 years or 100,000–150,000 miles. Check whether this warranty is transferable to new owners in your area. Be on the lookout for signs of trouble, such as charging speeds that slow down noticeably or fluctuate – these could point to thermal issues or imbalances in the battery cells.
Choosing the Right Battery Type for Your Needs
Now that you’re familiar with battery maintenance, the next step is choosing the right battery type for your vehicle. Knowing the differences between battery chemistries can help you make a smarter purchase, especially when browsing EV options on EV24.africa.
LFP vs. Other Battery Types: Which to Choose
In 2026, EV buyers typically choose between LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and nickel-based options like NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt). Each has its strengths, depending on your driving habits and the conditions you face.
LFP batteries are more affordable to produce, costing about 20% less than nickel-based cells. For example, LFP batteries are priced around $98.50/kWh, compared to $112.70/kWh for nickel alternatives. They also last longer, offering 2,500 to over 9,000 charge cycles, while nickel-based batteries typically provide 1,000 to 2,300 cycles. If you live in a hot climate or plan to keep your car for over a decade, LFP batteries are a solid choice due to their heat resistance and longevity. A study of used Tesla Model 3s with over 100,000 miles found that LFP-equipped vehicles retained 87–93% of their original battery health, whereas nickel-based batteries (specifically NCA) retained 71–83%.
"LFP batteries are interesting because they cost about 20% less to produce than other kinds of batteries… they’re cheap, tough little workhorses that are good at getting the job done." – Patrick George, Editor, InsideEVs
However, LFP batteries have their downsides. With 30% lower energy density, they are heavier and offer a shorter driving range compared to nickel-based options. If you frequently drive long distances or experience cold weather – where LFP performance tends to decline – a nickel-based battery may be a better fit.
Here’s a quick side-by-side comparison:
| Feature | LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Nickel-Based (e.g., NMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Hot climates, cost-conscious buyers, long-term ownership | Long-range travel, cold climates, performance |
| Cost | Lower (~$98.50/kWh) | Higher (~$112.70/kWh) |
| Cycle Life | 2,500 – 9,000+ cycles | 1,000 – 2,300 cycles |
| Energy Density | Lower (heavier pack, shorter range) | Higher (lighter, longer range) |
| Thermal Stability | High (runaway at 270°C) | Moderate (runaway at 210°C) |
| Charging Approach | Can charge to 100% regularly | Limit to 80–90% daily |
| Cold Weather | Performs poorly below freezing | Better range retention in cold weather |
If affordability and heat resistance are your priorities, LFP is the way to go. But if you need maximum range or consistent performance in cold weather, nickel-based batteries might be worth the extra cost.
How to Check Battery Details on EV24.africa
When comparing EV options online, take note of the following battery specifications to evaluate your choices effectively:
- Battery Chemistry: Look for terms like "LFP", "LiFePO4", or "Lithium Iron Phosphate" for LFP batteries, and "NMC", "NCA", or "Ternary Lithium" for nickel-based options. For Ford vehicles, you can confirm battery type by checking the VIN – if the 8th digit is a 4 or 5, it has an LFP battery.
- Battery Capacity: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), this indicates how much energy the battery can store. Keep in mind that LFP packs may be larger for the same range as nickel-based ones.
- Range Estimates: Check whether the range is EPA-rated (common in the U.S.) or WLTP-rated (used internationally). Remember, real-world conditions – especially extreme heat – can affect range.
- Fast-Charging Capabilities: Look for maximum DC charging speeds (in kilowatts) and supported connector types like CCS, CHAdeMO, or Tesla’s NACS, particularly if you rely on public charging stations.
- Warranty Terms: Verify whether the battery warranty is transferable to new owners in your area.
When buying an EV, ask the seller these key questions:
- What is the current battery health percentage?
- Has the battery been professionally tested?
- What is the charging history (e.g., mostly AC or DC fast charging)?
- Are there any documented thermal management issues?
- Is the manufacturer’s battery warranty still valid and transferable?
For used EVs, request a professional battery health report instead of relying solely on dashboard indicators. Considering that a full battery replacement in 2025 could cost anywhere from $6,000 for compact models to over $20,000 for luxury SUVs, understanding the battery’s condition upfront can save you from unexpected expenses later.
Next, let’s look at other important considerations for EV buyers in 2026.
What EV Buyers Should Remember in 2026
LFP batteries are changing the game for EVs. They stand out for their safety, affordability, and durability compared to traditional nickel-based batteries. If you live in a hot region or plan to keep your EV for many years, LFP batteries are a solid choice. That said, they do come with a trade-off: lower energy density. This means the battery packs are heavier, and you might see a slight reduction in range.
Charging habits make a difference. LFP batteries handle 100% charges better than nickel-based ones, but keeping them at 75%–100% charge for long periods can still speed up wear and tear. To keep your battery in good shape, aim to charge to 100% only weekly or monthly, as recommended by the manufacturer. Avoid leaving the battery fully charged in extreme heat (above 104°F [40°C]). For everyday use, try to keep the charge between 20% and 80%. When on road trips, use DC fast chargers sparingly and stop charging around 80% to save time and reduce stress on the battery. These habits not only extend your battery’s lifespan but also highlight the importance of knowing your battery’s specifications before you buy.
Double-check battery details before committing. Not all EVs clearly state their battery type. When browsing platforms like EV24.africa, confirm the battery chemistry, capacity (measured in kWh), fast-charging capabilities, and warranty terms. For used EVs, don’t just rely on the dashboard – request a professional battery health report. These steps, along with proper maintenance, ensure your EV performs well over the long term.
LFP batteries are gaining momentum in Africa. Thanks to their ability to handle high temperatures and their compatibility with solar systems, LFP batteries are particularly well-suited for areas with less developed infrastructure. Globally, LFP batteries have seen their market share jump from 6% in 2020 to 30% in 2022, with projections showing they could overtake nickel-based batteries by 2028. Platforms like EV24.africa can guide you through the process of checking maintenance tips, verifying battery specs, and making smart choices tailored to local conditions.
For buyers in warm climates, LFP batteries offer a strong mix of safety, cost-effectiveness, and durability. By adopting smart charging habits, verifying battery details, and using trusted resources, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the fast-changing EV market in 2026.
FAQs
What makes LFP batteries a better choice than nickel-based batteries for EV buyers in 2026?
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries bring some clear advantages for EV buyers in 2026, especially when compared to nickel-based options like NMC. One of the biggest perks? They’re more affordable. By using materials like iron and phosphate – both widely available – they avoid the high costs associated with metals like nickel and cobalt. This can cut battery costs by as much as 30%, making EVs easier on the wallet.
Safety is another strong point for LFP batteries. Thanks to their thermal stability, they’re far less likely to overheat or catch fire, offering peace of mind to drivers and passengers alike.
Durability is where LFP batteries truly shine. They can handle more charge and discharge cycles than their nickel-based counterparts, translating to fewer replacements and a longer lifespan overall. Plus, their chemistry allows for full charges without the risk of damage, simplifying charging routines and making them more dependable for everyday use.
For EV buyers in 2026, particularly in areas where cost and reliability matter most, LFP batteries are a smart choice. They’re affordable, long-lasting, and require less maintenance, ticking all the boxes for drivers looking for a practical and dependable option.
Does fast charging affect the lifespan of LFP batteries compared to other types?
Fast charging can affect the lifespan of LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries, but they handle the stress much better than nickel-based alternatives. Thanks to their stability and resistance to heat, LFP batteries experience less wear and tear from fast charging, resulting in a slower loss of capacity over time.
Although frequent fast charging can raise the battery’s temperature and slightly accelerate aging, research shows that LFP batteries still outlast nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) batteries under these conditions. Charging all the way to 100% may contribute to a bit more degradation, but for most drivers, this impact is minor – especially if you stick to charging between 75-80% for everyday use.
For EV owners who depend on fast charging, LFP batteries stand out as a reliable choice, offering better durability and a longer lifespan under high-current charging compared to other battery types.
How can I keep my LFP battery in good condition in hot climates?
To keep your Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) battery in good shape, especially in hot climates, it’s crucial to manage both temperature and charging practices. Avoid charging when the temperature exceeds 95°F, and try not to leave your car parked in direct sunlight for extended periods. If you must charge in warm weather, opt for slower charging speeds to reduce heat buildup, and park in shaded or well-ventilated spots when possible.
For daily use, aim to maintain the battery’s state of charge (SOC) between 20% and 80%. This range helps ease the strain on the battery cells. Regularly charging to 100% or letting the charge drop below 20% can wear down the battery over time. If you’re not planning to use the vehicle for a while, store it in a moderate environment (around 68°F) with the SOC close to 50%. This will help maintain the battery’s capacity.
Other simple practices can go a long way. Pre-cool the car before charging, check connectors for signs of corrosion, and keep the battery free of dust and debris. These small steps can help ensure your LFP battery stays reliable and lasts longer, even in challenging heat conditions.




