Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining traction in Africa, offering a cleaner, renewable-powered alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel cars. With growing urban populations, climate concerns, and heavy reliance on imported petroleum, EVs present a solution to reduce emissions, improve air quality, and cut energy costs. However, challenges like high costs, limited charging infrastructure, and grid instability slow progress. Governments are stepping in with tax breaks, while local manufacturing and battery recycling initiatives are emerging as potential game-changers.
Key Highlights:
- EV Demand Drivers: Urban growth, climate issues, and renewable energy potential.
- Challenges: High purchase costs, limited charging stations, and misconceptions about EVs.
- Opportunities: Local manufacturing in countries like Ethiopia, Ghana, and South Africa; battery recycling programs in Kenya and South Africa.
- Infrastructure Solutions: Solar and wind-powered charging stations to address grid issues.
Africa’s shift toward EVs is not just about cleaner transport but also economic growth through local production and renewable energy integration.
4 Business Strategies Changing Africa’s EV Game
Current Trends in African Electric Vehicle Adoption
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption is gaining momentum across Africa, driven by the rapid growth of urban areas and the increasing need to address climate challenges. This shift has prompted governments and technology innovators to take action, shaping a dynamic and evolving market.
Expanding Cities and Climate Challenges Spark EV Demand
As cities across Africa continue to grow, the demand for cleaner and more efficient transportation solutions is on the rise. Concerns about climate change are influencing decisions, with stakeholders prioritizing vehicles that align with sustainability goals while meeting local needs.
Supportive Government Policies and Tax Incentives
African governments are stepping up with policies designed to make EVs more accessible. These include tax breaks and other incentives aimed at reducing the cost of entry for both consumers and businesses. By tying environmental objectives to economic strategies, these initiatives are not only promoting greener transportation but also creating opportunities for infrastructure development and investment. This dual focus is helping to build a foundation for long-term growth in the EV sector.
Advances in EV Technology and Locally Relevant Solutions
Technological progress is addressing key concerns like battery performance, range, and durability, making EVs more practical for everyday use. Local initiatives are also playing a significant role, offering vehicles tailored to regional conditions and needs. These advancements are helping individuals and businesses overcome traditional barriers to EV adoption, while also paving the way for future opportunities in local manufacturing and job creation. Together, these developments are reshaping the mobility landscape across the continent.
Building EV Infrastructure and Clean Energy Systems
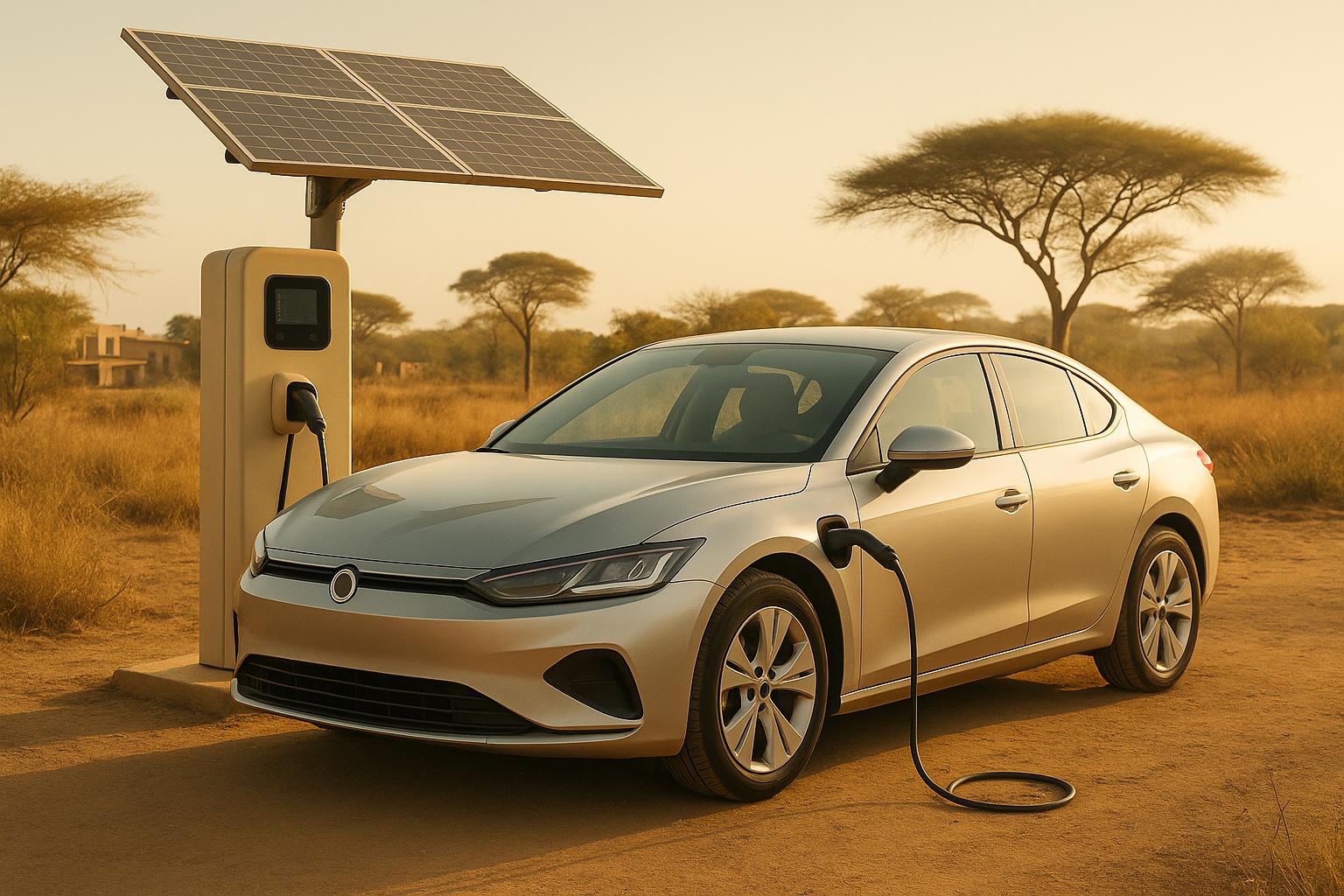
The growth of electric vehicle (EV) adoption in Africa hinges on the development of a reliable charging infrastructure. While urban centers are making strides, rural regions with unstable power grids are falling behind. Tapping into renewable energy sources offers a way to bridge this gap and promote sustainable transportation. Let’s dive into the current state of charging solutions and how renewable energy is reshaping the landscape.
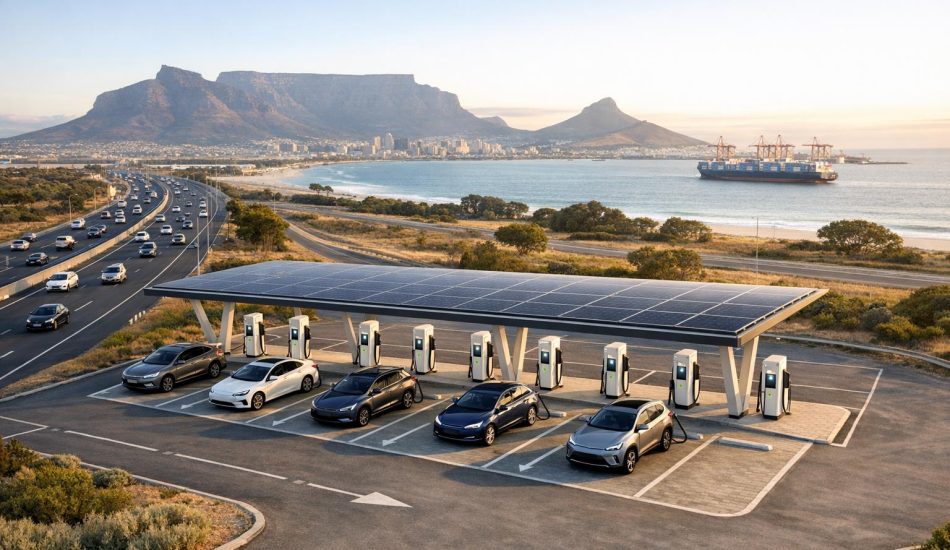
Expanding Charging Networks
Africa’s charging infrastructure paints a stark contrast between bustling cities and remote areas. Urban hubs are steadily growing their charging networks, but rural and middle-income areas remain underserved. Most installations are clustered in commercial zones and affluent neighborhoods, leaving significant portions of the population without access.
The pace of expansion is slowed by steep installation costs, unreliable power supplies, and frequent outages, all of which compromise the dependability of charging stations. In rural areas, the challenges are even greater. Sparse populations and weak grid systems discourage investment, creating a cycle where potential EV buyers hesitate, and developers hold back until adoption rates improve.
Creative solutions are beginning to emerge. Mobile charging units, which provide on-demand services, are gaining traction in several countries. Additionally, collaborations between governments and private companies are picking up speed. Some initiatives are targeting strategic spots like highways and major transport routes, which are critical for unlocking the continent’s EV potential.
Beyond just building more stations, renewable energy is transforming how these networks function.
Powering EV Charging with Solar and Wind Energy
Africa’s rich renewable energy resources offer a unique chance to power EV charging stations while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. With abundant sunlight, solar-powered charging stations equipped with battery storage are a practical solution, especially in areas prone to outages or limited grid access.
Coastal regions, with their strong winds, can integrate wind power into charging systems. Combining solar and wind energy in hybrid setups not only stabilizes energy output but also reduces the need for costly battery storage. This dual approach aligns with environmental goals and lowers operational costs.
Renewable systems can also feed surplus energy back into the grid during off-peak times. This creates additional revenue for charging station operators and improves grid stability. In areas with unreliable power, these systems can double as local energy hubs, supplying electricity to businesses and essential services beyond EV charging.
Smart charging technologies further enhance the efficiency of renewable-powered systems. By syncing charging schedules with renewable energy availability, weather patterns, and electricity rates, these systems ensure maximum use of clean energy while keeping costs down for both operators and EV owners.
sbb-itb-99e19e3
Barriers to EV Adoption in Africa
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption across Africa faces significant hurdles, including high costs, limited charging infrastructure, and persistent misconceptions. These challenges create a complex landscape that slows down the transition to EVs.
High Costs and Limited Financing Options
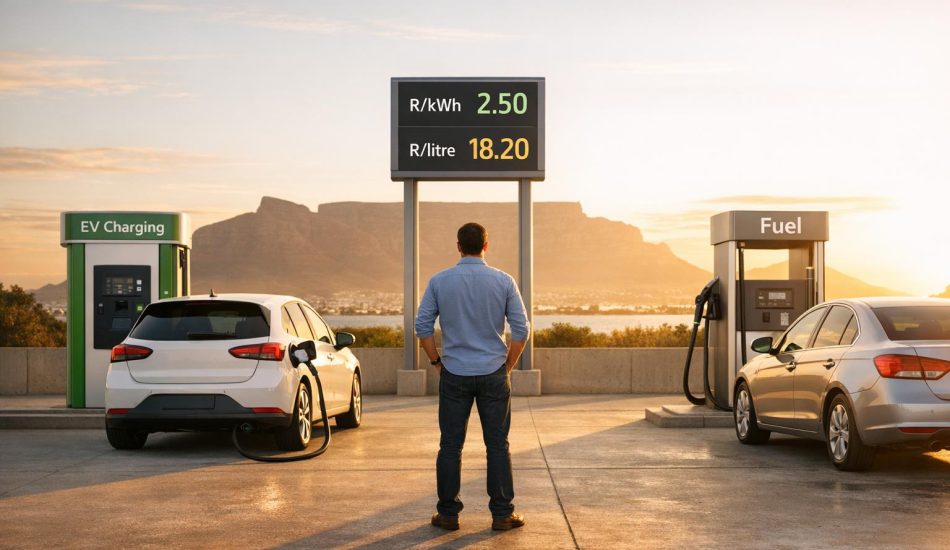
The financial aspect is one of the biggest barriers to EV adoption. With high upfront costs, EVs are often seen as a luxury item, even as more affordable models and better financing options are introduced. Vehicles like the BYD Dolphin and GWM Ora are beginning to shift this perception, with some models expected to fall below $40,000 as local manufacturing ramps up and import taxes decrease. While EVs promise long-term savings on operating costs, the initial investment remains out of reach for many potential buyers.
Few Charging Stations and Power Grid Issues
The lack of widespread charging infrastructure is another significant obstacle. Although urban areas are starting to expand their charging networks, many regions still struggle with inconsistent and unreliable coverage. On top of that, frequent power outages and grid instability – often caused by load-shedding – add to consumers’ range anxiety. These challenges not only discourage buyers but also slow the pace of infrastructure development.
Misconceptions and Limited Knowledge About EVs
Misunderstandings about electric vehicles also play a role in slowing adoption. Many people still view EVs as vehicles only for the wealthy, despite the increasing availability of more affordable options. Concerns about battery lifespan, doubts about performance – such as power and acceleration – and a lack of trained service providers further add to the hesitation. These misconceptions highlight the need for public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the benefits and practicality of EVs. Bridging these knowledge gaps will be essential as Africa works toward greater adoption and improved infrastructure.
Growth Opportunities: Local Manufacturing and Battery Recycling
Countries around the world are beginning to see the potential for building their own electric vehicle (EV) industries. By focusing on local manufacturing and battery recycling, they can stimulate economic growth while addressing sustainability challenges.
Building EVs Locally and Creating Jobs
With supportive policies and advancements in technology, local EV manufacturing has become a powerful driver of growth. Several African nations are stepping up to establish themselves as leaders in this space:
- Ethiopia has taken a bold step by banning internal combustion engine imports, a move expected to drive electric vehicle sales to over 60% by early 2025. This policy shift is attracting international manufacturers eager to set up local assembly operations.
- Ghana is offering an eight-year zero-tariff window for fully electric imports, a strategy designed to attract global original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to invest in local assembly facilities. This approach balances the need to build manufacturing capacity while keeping EVs affordable during the transition.
- South Africa is leveraging its well-established automotive industry with production rebates aimed at encouraging local EV manufacturing. Its existing supply chains and skilled workforce provide a solid foundation for EV assembly and battery production.
- Morocco has positioned itself as a prime destination for battery manufacturing, thanks to its proximity to European markets and access to renewable energy. The country’s industrial zones are drawing significant investments for battery plants that can cater to both African and European markets.
Investing in local manufacturing not only creates direct jobs in assembly but also generates indirect roles in logistics, maintenance, and support. It attracts foreign investment, helps workers develop new skills, and fosters innovation in the automotive sector.
Recycling EV Batteries and Reducing Waste
As the number of electric vehicles on the road increases, so does the need for effective battery recycling and reuse programs. Even when EV batteries are no longer suitable for vehicles, they still hold enough capacity to be repurposed for other applications, such as stationary energy storage.
Early efforts in South Africa and Kenya are already showing promise, with pilot projects repurposing used EV batteries for off-grid and microgrid energy systems. These initiatives not only support renewable energy integration but also promote a circular economy for EV components.
Recycling EV batteries offers several benefits, including recovering valuable materials, reducing dependency on raw material imports, and making energy storage more affordable. Additionally, recycling helps address environmental concerns by keeping batteries out of landfills and extending their useful life.
The recycling industry is poised for growth as Africa’s EV market is expected to generate $263.1 million in revenue by 2025, with a projected annual growth rate of 8.5% through 2030. With EV sales potentially exceeding 7,000 units by 2030, the volume of batteries available for recycling will create significant business opportunities.
As manufacturing and recycling systems expand, efficient distribution channels will be key to scaling these efforts.
How EV24.africa Helps Buyers Access Electric Vehicles
While local manufacturing gains momentum, platforms like EV24.africa are making it easier for buyers to access electric vehicles. The marketplace offers a wide range of options from manufacturers such as Tesla, BYD, Leapmotor, Dongfeng, Geely, Hyundai, Toyota, and Suzuki.
EV24.africa simplifies the process by managing logistics, including shipping, customs clearance, and local registration across all 54 African countries. The platform also provides tailored financing options and transparent pricing, complete with detailed vehicle specifications.
As domestic manufacturing grows, EV24.africa can play a vital role in connecting local manufacturers with consumers, creating a seamless distribution network. This combination of local production and efficient distribution will be crucial for accelerating EV adoption across Africa.
Conclusion: Africa’s Electric Vehicle Future
Africa stands at the edge of a transportation shift, fueled by a mix of supportive government policies, private sector investment, and growing consumer interest. Across the continent, several countries are already taking steps to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), with some positioning themselves as early leaders in manufacturing. To truly unlock this potential, collaboration among policymakers, businesses, and consumers is essential to tackle challenges like affordability, infrastructure gaps, and public perception.
One key opportunity lies in expanding charging networks powered by renewable energy. With Africa’s vast solar and wind resources, these networks could leapfrog traditional automotive systems, offering a cleaner and more efficient alternative. This approach not only supports EV adoption but also creates a foundation for an integrated market where local production and recycling spur economic growth. By focusing on manufacturing and battery recycling, the continent can generate jobs, reduce reliance on imports, and strengthen its industrial base. Platforms like EV24.africa are well-positioned to bridge the gap between manufacturers and consumers, fostering connections across the region.
Africa’s journey toward an electric vehicle future goes beyond transportation – it’s about building a resilient and sustainable economy. By combining renewable energy, homegrown production, and innovative recycling practices, the continent has a real chance to carve out a significant role in the global EV movement.
FAQs
What challenges are slowing down electric vehicle adoption in Africa, and how can they be addressed?
The journey toward adopting electric vehicles (EVs) in Africa is not without its hurdles. High costs, a lack of charging infrastructure, and a heavy dependence on imports are some of the main obstacles standing in the way. For many consumers, EVs remain out of reach financially, and the absence of robust financing options only deepens the challenge. On top of that, the limited availability of public charging stations – combined with unreliable electricity in many areas – fuels “range anxiety,” making potential buyers hesitant to make the switch.
There are, however, ways to tackle these challenges. Governments could step in by offering tax breaks, subsidies, and lower import duties, which would help make EVs more affordable. Expanding charging networks, particularly those powered by renewable energy, could ease concerns about charging availability. Educating communities through public awareness campaigns might also bridge the knowledge gap, highlighting the benefits of EVs while addressing common misunderstandings. Another promising approach is to promote local production or assembly of EVs. This strategy could reduce costs, generate employment, and provide a boost to local economies.
How are African nations using renewable energy to expand electric vehicle infrastructure?
African nations are making strides toward incorporating renewable energy sources – such as solar, wind, and hydropower – to support the development of electric vehicle (EV) charging networks. This shift aims to minimize dependence on fossil fuels while reducing the carbon emissions associated with EV operations.
In regions with plentiful sunlight, solar-powered charging stations are becoming increasingly common. These stations not only promote cleaner energy use but also tackle issues like unreliable electricity access in certain areas. This approach is helping to create a more sustainable and accessible EV infrastructure across the continent.
How do local manufacturing and battery recycling impact the growth of electric vehicles in Africa?
Local manufacturing and battery recycling are key to advancing the future of electric vehicles (EVs) in Africa. Building EVs locally can cut down on import expenses, generate employment, and nurture technical skills, ultimately making electric mobility more affordable and accessible to everyday consumers.
Equally vital is battery recycling, which helps create a sustainable EV ecosystem. Recycling minimizes environmental waste, preserves critical materials like lithium and cobalt, and reduces the overall cost of producing batteries. These combined efforts pave the way for a cleaner and more self-sufficient future for electric mobility across the continent.




